The Role of Laser Therapy in Healing Tendonitis and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries
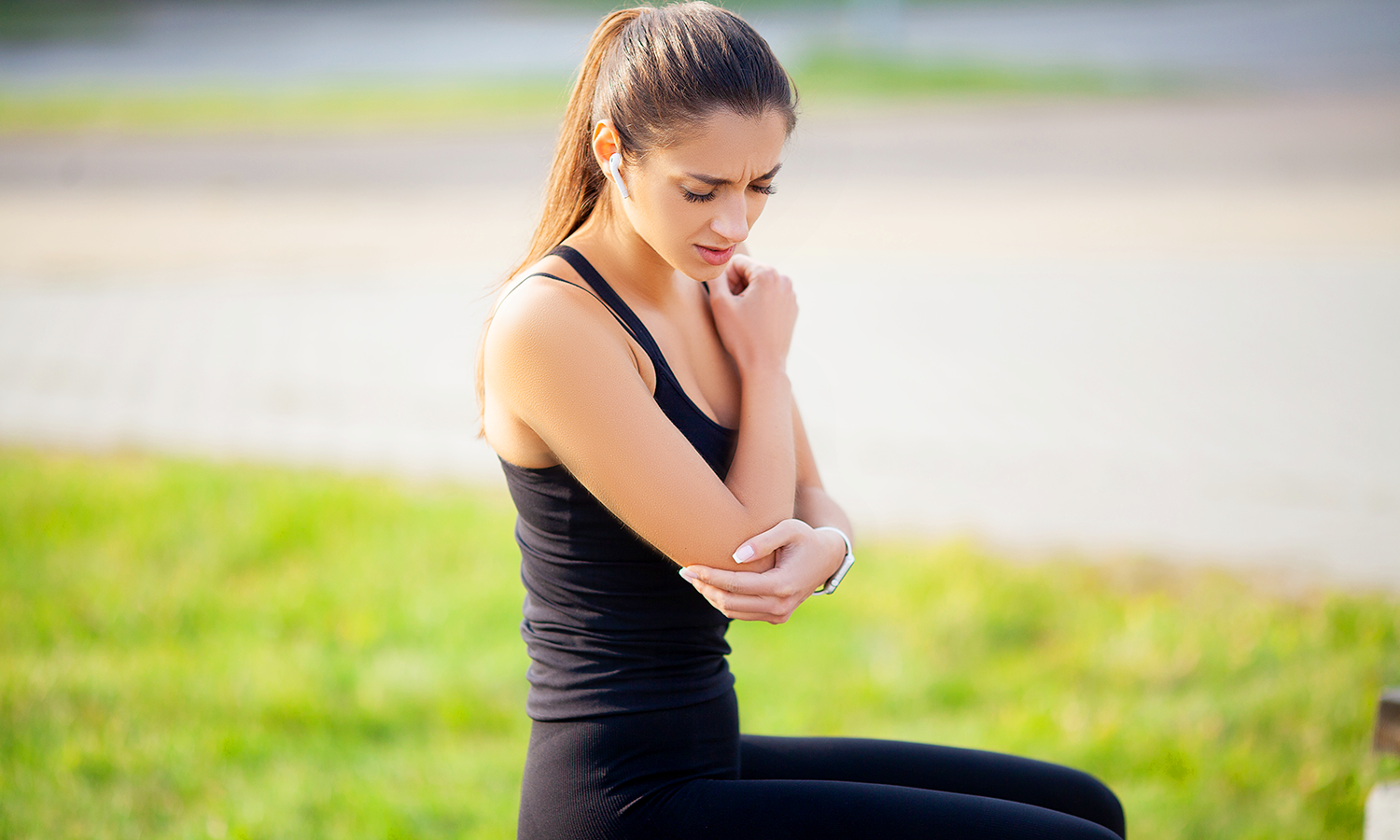
Laser therapy has emerged as one of the most innovative and effective treatments for a wide range of musculoskeletal injuries. Whether it’s a minor strain or a chronic condition like tendonitis, laser therapy offers a non-invasive approach to healing that accelerates recovery while minimizing pain and inflammation.
1. Introduction to Laser Therapy for Soft-Tissue Injuries and Tendonitis
1.1 What Is Laser Therapy?
Laser therapy, also known as photobiomodulation (PBM), is a non-invasive treatment that uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate healing in injured or inflamed tissues. The light energy is absorbed by the cells, which then use this energy to speed up the body’s natural healing processes. Laser therapy works by increasing circulation, reducing inflammation, and promoting tissue repair at the cellular level. It is commonly used for a variety of conditions, including tendonitis, muscle strains, and joint injuries.
Unlike traditional therapies such as heat or cold packs, laser therapy penetrates deep into the tissue to target the root cause of the problem. It’s often considered a more advanced and effective approach to pain management and healing because of its ability to reach the underlying tissue without causing harm or discomfort.
1.2 Types of Laser Therapy Used for Tendonitis
There are several types of laser therapy, each with its own method of action and range of applications. The most common types used for tendonitis and soft-tissue injuries include:
Cold Laser Therapy (Low-Level Laser Therapy – LLLT): Cold lasers use low-powered light (less than 500 mW) to penetrate the skin and promote healing. It does not generate heat, making it a gentle option for treating inflammation and pain. Cold laser therapy is typically used for superficial injuries and conditions such as tendonitis, bursitis, and muscle strains.
High-Level Laser Therapy (Class IV Laser Therapy): High-level lasers use higher power output (greater than 500 mW) to penetrate deeper into the tissue. These lasers are ideal for treating deeper injuries and chronic conditions that require a higher dose of light energy. High-level laser therapy is often used for more severe soft-tissue injuries, post-surgical recovery, and conditions like chronic tendonitis.
1.3 Benefits of Laser Therapy in Soft-Tissue Healing
Laser therapy offers numerous benefits, especially when it comes to soft-tissue healing. Here are some of the key advantages:
Pain Reduction: Laser therapy helps to reduce pain by stimulating the production of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers. It also decreases the nerve’s ability to transmit pain signals.
Reduced Inflammation: One of the primary benefits of laser therapy is its ability to reduce inflammation. By increasing circulation and encouraging the lymphatic system to remove waste products, laser therapy helps to reduce swelling and tissue irritation.
Faster Healing: Laser therapy accelerates the production of collagen, an essential protein for tissue repair. It also enhances cellular metabolism, which speeds up the healing process for injured tissues.
Improved Circulation: By increasing blood flow to the affected area, laser therapy helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues, which accelerates healing.
2. How Laser Therapy Accelerates Healing in Tendonitis
2.1 Reducing Inflammation with Laser Therapy
One of the most effective ways laser therapy helps in tendonitis treatment is by reducing inflammation. Tendonitis is often characterized by swelling, heat, and redness in the affected tendon. Laser light stimulates the mitochondria in cells, boosting their energy production. This process helps the body fight inflammation more effectively and improves tissue function. Through this mechanism, laser therapy can significantly reduce the swelling and pain associated with tendonitis, allowing the tendon to heal faster.
2.2 Promoting Collagen Production for Tendon Repair
Collagen is the primary building block of tendons and other connective tissues. Laser therapy stimulates fibroblasts (cells that produce collagen) to increase collagen production. As collagen is the key protein responsible for tendon repair, increasing its production speeds up the healing process for injured tendons. This is especially important in conditions like tendonitis, where the tendon fibers are damaged and need to be rebuilt.
2.3 Pain Relief and Improved Mobility
Laser therapy is known for its pain-relieving effects. By stimulating the release of endorphins, it helps reduce the perception of pain in the treated area. Furthermore, by improving circulation and reducing inflammation, laser therapy enhances the mobility of the affected area, making it easier for patients to move their joints and tendons without pain. This is crucial for people suffering from tendonitis, where stiffness and discomfort can significantly limit movement.
3. Laser Therapy for Other Common Soft-Tissue Injuries
3.1 Laser Therapy for Muscle Strains and Sprains
Muscle strains and sprains are common soft-tissue injuries that cause pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion. Laser therapy can be used to treat these injuries by promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation. The light energy helps to stimulate the healing of muscle fibers, leading to faster recovery and reduced downtime. Studies have shown that laser therapy can be an effective treatment for muscle strains, helping patients recover quicker and experience less pain.
3.2 Tendon and Ligament Injuries: How Laser Therapy Helps
In addition to treating tendonitis, laser therapy is also beneficial for other tendon and ligament injuries, such as tears, strains, and sprains. The deep tissue penetration of high-level lasers makes it an ideal treatment for repairing torn or stretched tendons and ligaments. By stimulating collagen production and enhancing blood flow to the area, laser therapy speeds up the repair of these critical tissues.
3.3 Post-Surgical Recovery with Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is also commonly used in post-surgical rehabilitation. After tendon or ligament surgery, the healing process can be slow and painful. Laser therapy helps reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation, while also promoting collagen production to support tissue repair. Studies show that laser therapy can significantly accelerate recovery after soft-tissue surgeries like tendon repairs or ligament reconstructions.
4. Scientific Evidence and Studies Supporting Laser Therapy for Soft-Tissue Injuries
4.1 Clinical Trials on Laser Therapy for Tendonitis
Numerous clinical studies and trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of laser therapy in treating tendonitis. Research published in journals like Photomedicine and Laser Surgery has shown that laser therapy can reduce pain and inflammation in patients with tendonitis, improving their range of motion and overall quality of life. These studies have provided strong evidence that laser therapy is an effective non-invasive treatment for chronic tendon injuries.
4.2 Laser Therapy vs. Traditional Treatments for Soft-Tissue Injuries
When compared to traditional treatments like physical therapy, medications, or corticosteroid injections, laser therapy often provides faster relief with fewer side effects. Unlike medication, which may involve harmful side effects or require long-term use, laser therapy is non-invasive and generally well-tolerated by patients. Additionally, laser therapy can be used alongside other treatments, enhancing their effectiveness and speeding up recovery.
4.3 Patient Success Stories and Testimonials
Many patients who have undergone laser therapy for tendonitis and soft-tissue injuries report significant improvements in pain management and recovery times. For example, athletes recovering from injuries have shared their success stories, highlighting how laser therapy helped them return to their sport faster. Testimonials from patients with chronic tendonitis and other soft-tissue injuries also emphasize the treatment’s ability to alleviate pain and enhance mobility.
5. Is Laser Therapy Right for You? Considerations and Recommendations
5.1 When Should You Consider Laser Therapy?

MateLaser X1 Performance
$5,999.00
Accelerate healing and relieve pain with laser therapy – the proven solution for tendonitis and soft-tissue injuries.
View ProductLaser therapy is suitable for a wide range of soft-tissue injuries, including tendonitis, muscle strains, ligament injuries, and post-surgical recovery. Ideal candidates for laser therapy include individuals who experience chronic pain, inflammation, or stiffness in their tendons or muscles. It is particularly beneficial for those who want to avoid surgery or long-term medication use. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if laser therapy is appropriate for your specific condition.
5.2 Risks and Side Effects of Laser Therapy
While laser therapy is generally considered safe, there are a few potential risks and side effects. These may include mild skin irritation or sensitivity to light. In rare cases, improper use of the device or overuse may lead to temporary discomfort. It’s important to have a trained professional administer laser therapy to ensure proper technique and dosage. Pregnant women, individuals with certain medical conditions, or those with a history of cancer should consult a doctor before undergoing laser therapy.
5.3 How to Get Started with Laser Therapy for Soft-Tissue Injuries
If you are interested in trying laser therapy, the first step is to consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in pain management or rehabilitation. They can assess your injury, recommend an appropriate treatment plan, and refer you to a qualified practitioner. Many clinics now offer laser therapy as part of their physical therapy or pain management services. Be sure to inquire about the cost, the type of laser used, and the expected number of sessions needed for optimal results.
Laser therapy has proven to be a highly effective treatment for tendonitis and other soft-tissue injuries. By reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting faster healing, it provides a non-invasive and drug-free alternative to traditional treatments. With scientific evidence supporting its efficacy, laser therapy is a valuable option for anyone looking to recover quickly and improve their quality of life. Whether you are recovering from an injury or managing a chronic condition, laser therapy may be the key to faster, more effective healing.
6. References
The effects of laser treatment in tendinopathy: a systematic review
Biomechanical and biochemical protective effect of low-level laser therapy for Achilles tendinitis